The Role of Blockchain in Healthcare: Current and Future Applications
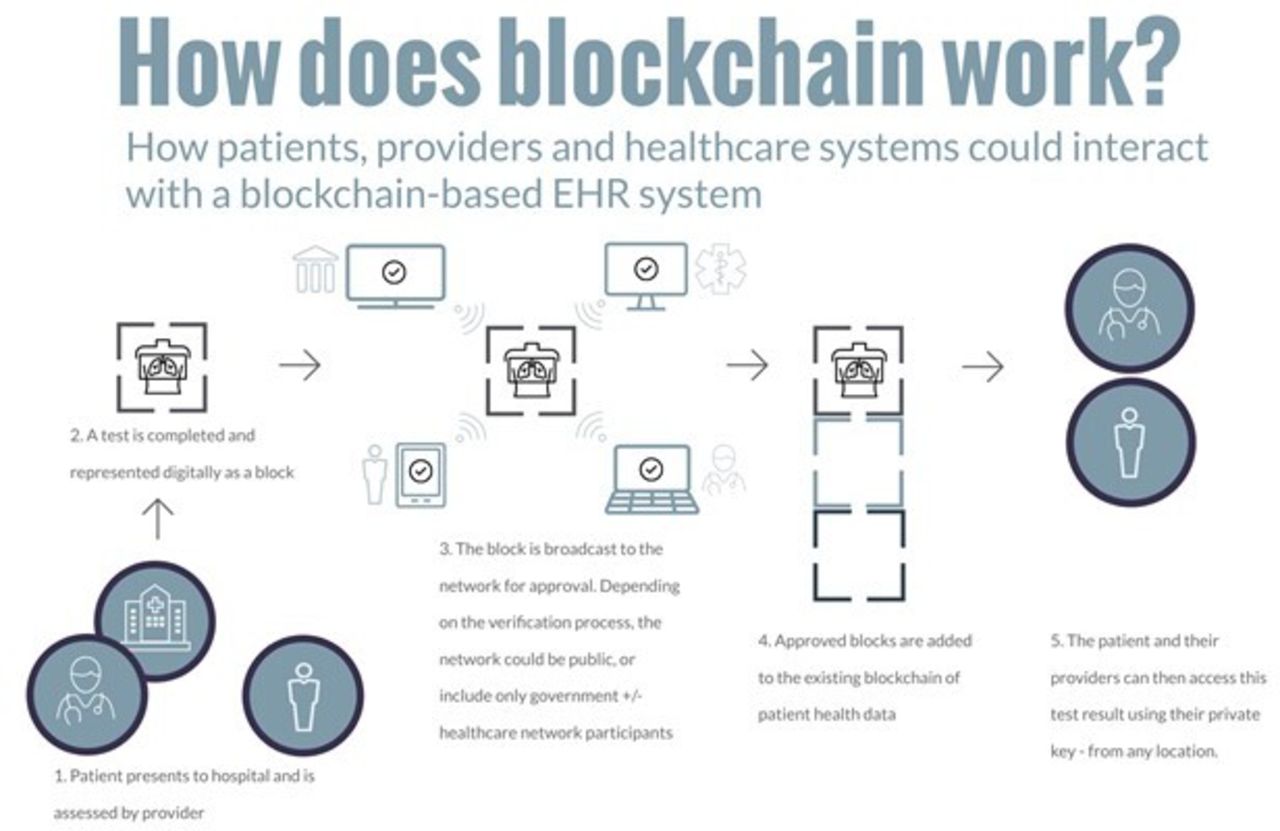
- Understanding Blockchain Technology in Healthcare
- Current Applications of Blockchain in the Healthcare Industry
- Benefits of Implementing Blockchain in Healthcare
- Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain Adoption in Healthcare
- Future Potential of Blockchain Technology in Revolutionizing Healthcare
- Regulatory Considerations for Blockchain Implementation in Healthcare
Understanding Blockchain Technology in Healthcare
Blockchain technology in healthcare is revolutionizing the way patient data is stored and shared securely. By utilizing a decentralized and encrypted ledger system, blockchain ensures that sensitive information remains private and tamper-proof. This technology has the potential to streamline processes, reduce costs, and improve the overall quality of care for patients.
One of the key benefits of blockchain in healthcare is its ability to create a single source of truth for patient data. This means that all relevant information, such as medical records, test results, and treatment plans, can be accessed in real-time by authorized healthcare providers. This not only improves the efficiency of care delivery but also reduces the risk of errors and duplication.
Moreover, blockchain technology can enhance data security by encrypting information and providing a transparent audit trail of who has accessed it. This can help prevent data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive patient information. Additionally, blockchain can facilitate interoperability between different healthcare systems, allowing for seamless data exchange and collaboration among providers.
Overall, the potential applications of blockchain in healthcare are vast and promising. From improving data security and interoperability to streamlining processes and reducing costs, this technology has the power to transform the healthcare industry for the better. As more healthcare organizations adopt blockchain solutions, patients can expect to see increased transparency, efficiency, and quality of care in the future.
Current Applications of Blockchain in the Healthcare Industry
Blockchain technology has been making waves in the healthcare industry, offering innovative solutions to long-standing challenges. Some of the current applications of blockchain in healthcare include:
- **Secure** sharing of medical records: Blockchain allows for the secure and **immutable** storage of patient data, ensuring that sensitive information is protected from **unauthorized** access.
- Streamlining **clinical** trials: By using blockchain, researchers can **verify** the authenticity of data collected during **clinical** trials, reducing the risk of **fraud** and **improving** the overall efficiency of the process.
- Supply chain management: Blockchain can be used to track the **movement** of pharmaceuticals and medical devices throughout the supply chain, **ensuring** transparency and reducing the risk of counterfeit products entering the market.
- **Smart** contracts for **insurance** claims: **Smart** contracts can automate the **claims** process for **insurance** providers, **reducing** the time and **cost** associated with **processing** claims and **minimizing** the risk of **fraud**.
These are just a few examples of how blockchain is **transforming** the healthcare industry, **providing** new opportunities for **improving** **efficiency** and **security**. As the technology continues to **evolve**, we can expect to see even more **innovative** applications of blockchain in healthcare in the future.
Benefits of Implementing Blockchain in Healthcare
Implementing blockchain technology in healthcare offers a wide range of benefits that can revolutionize the industry. Some of the key advantages include:
- Enhanced security: Blockchain provides a secure and tamper-proof way of storing and sharing patient data, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
- Improved interoperability: By using blockchain, healthcare providers can easily share patient information across different systems and organizations, leading to better coordination of care.
- Increased transparency: The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that all transactions are recorded and can be accessed by authorized parties, promoting transparency in healthcare operations.
- Streamlined processes: Blockchain can automate and streamline various administrative tasks, such as billing and claims processing, leading to cost savings and efficiency improvements.
- Enhanced data integrity: With blockchain, patient data is stored in a secure and immutable way, ensuring its accuracy and reliability for clinical decision-making.
Overall, the implementation of blockchain in healthcare has the potential to transform the industry by addressing key challenges related to data security, interoperability, transparency, and efficiency. As more healthcare organizations adopt this technology, we can expect to see significant improvements in patient care and outcomes.
Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain Adoption in Healthcare
There are several challenges and limitations that hinder the widespread adoption of blockchain technology in the healthcare industry. Despite its potential benefits, there are still barriers that need to be addressed in order to fully leverage the capabilities of blockchain in healthcare:
- **Interoperability**: One of the main challenges is the lack of interoperability between different blockchain platforms and existing healthcare systems. This makes it difficult to seamlessly share and access patient data across various providers and organizations.
- **Regulatory Compliance**: The healthcare industry is highly regulated, and implementing blockchain technology requires compliance with strict data privacy and security regulations such as HIPAA. Ensuring that blockchain solutions meet these regulatory requirements can be a complex and time-consuming process.
- **Scalability**: Blockchain networks can face scalability issues when it comes to processing a large volume of transactions, especially in a data-intensive industry like healthcare. This can lead to delays and inefficiencies in accessing and updating patient records.
- **Cost**: Implementing blockchain technology in healthcare can be costly, both in terms of initial investment and ongoing maintenance. This can be a barrier for smaller healthcare providers or organizations with limited resources.
- **Security Concerns**: While blockchain is known for its security features, it is not immune to cyber threats and vulnerabilities. Ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of patient data stored on a blockchain network is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of blockchain technology in healthcare are significant. By addressing these limitations and finding solutions to overcome them, the healthcare industry can unlock the full potential of blockchain to improve data security, interoperability, and transparency in patient care.
Future Potential of Blockchain Technology in Revolutionizing Healthcare
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the healthcare industry in the future by addressing various challenges and improving efficiency. One of the key benefits of blockchain in healthcare is its ability to securely store and share patient data across different healthcare providers. This can lead to better coordination of care, reduced medical errors, and improved patient outcomes.
Furthermore, blockchain can help in streamlining administrative processes such as billing and claims processing by providing a transparent and tamper-proof record of transactions. This can reduce fraud and errors, ultimately leading to cost savings for both healthcare providers and patients.
Another area where blockchain technology can make a significant impact is in clinical trials and research. By using blockchain to securely store and share data, researchers can ensure the integrity and authenticity of their findings, leading to more reliable research outcomes. This can accelerate the development of new treatments and therapies, benefiting patients worldwide.
In addition, blockchain can also facilitate the implementation of smart contracts in healthcare, automating processes such as insurance claims and payments. This can help in reducing administrative costs and improving the overall efficiency of the healthcare system.
Overall, the future potential of blockchain technology in revolutionizing healthcare is vast. By leveraging the security, transparency, and efficiency of blockchain, the healthcare industry can overcome many of its current challenges and provide better care to patients around the world.
Regulatory Considerations for Blockchain Implementation in Healthcare
When considering the implementation of blockchain technology in healthcare, it is crucial to take into account the various regulatory considerations that come into play. The healthcare industry is heavily regulated to ensure patient safety, data privacy, and compliance with laws such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States. Blockchain implementation must adhere to these regulations to maintain trust and integrity within the healthcare system.
One of the main regulatory considerations for blockchain implementation in healthcare is data privacy. Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent way to store and share data, but it must also comply with regulations that protect patient information. Ensuring that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive data is essential to maintaining patient confidentiality and trust in the system.
Another important regulatory consideration is data security. Blockchain technology can help prevent data breaches and unauthorized access by providing a tamper-proof and decentralized system. However, healthcare organizations must still comply with regulations that govern data security to protect against cyber threats and ensure the integrity of patient information.
Additionally, regulatory considerations for blockchain implementation in healthcare include interoperability and standardization. Healthcare systems often use different formats and protocols for data exchange, making it challenging to share information seamlessly. Blockchain technology can help address these issues by providing a standardized and interoperable platform for data sharing, but it must align with existing regulations and standards to ensure compatibility and compliance.




